Are you ready to explore the fascinating world of women’s healthcare in Canada? Whether you’re a long-time resident or a newcomer to the country, navigating the healthcare system’s ins and outs can be exciting and daunting. But don’t worry, you’re in good hands. In this blog post, we’ll demystify everything you need to know about women’s health and wellness in Canada.
From understanding the unique needs of women to exploring the range of services available, we’ll delve into the strengths and areas for improvement of the healthcare system. So get ready to empower yourself with the knowledge to access and utilize the healthcare resources available for women effectively. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Women’s Health Needs in Canada
Women’s health in Canada encompasses a spectrum of needs, from reproductive health to mental well-being. It’s crucial to recognize that women’s health issues are not just biologically different from men’s but also influenced by social, cultural, and economic factors. In Canada, a focus on Women’s wellness services ensures that healthcare is reactive and proactive, dealing with the prevention and early detection of diseases common in women.
Issues like breast and cervical cancer, osteoporosis, and heart disease, which disproportionately affect women, are a priority. Moreover, the recognition of the unique mental health challenges faced by women has led to more tailored services in this area. Understanding these diverse needs is the first step in ensuring accessible healthcare in Canada for women.
Basic Structure of the Canadian Healthcare System
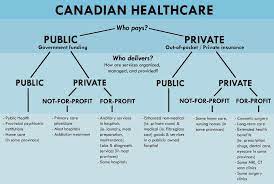
The Canadian healthcare system is a complex yet well-integrated network of services that provide comprehensive care to all citizens, including Canadian women’s healthcare needs. Primarily funded by the government, healthcare in Canada ensures basic coverage for all, including access to hospitals, doctors, and certain medical tests and treatments. Each province and territory may have different specifics regarding additional services covered.
Women’s preventive care in Canada, including regular health screenings like mammograms and Pap tests, is generally covered under the public health system. However, certain aspects of women’s health, such as specific fertility treatments and some mental health services, might not be fully covered, necessitating a mix of public and private healthcare provisions. Understanding this structure helps navigate the system and access the right services at the right time
How the System Caters to Women’s Health: Services Covered and Those Not Covered
The Canadian healthcare system provides various services catering to women’s health. However, there are also notable gaps in coverage.
Services Typically Covered:
- General Health Check-ups and Consultations: Regular medical appointments, including annual physicals, are fully covered.
- Maternal Healthcare: This includes comprehensive prenatal check-ups, ultrasound scans, delivery (both normal and cesarean), and postnatal care.
- Preventive Screenings: Screenings for breast and cervical cancer (mammograms and Pap smears) and osteoporosis (bone density tests) are routinely covered.
- Basic Reproductive Health Services: Services like contraceptive advice, STI testing, and certain aspects of fertility treatments.
- Hospital Services include all necessary in-hospital treatments like surgeries, emergency care, and inpatient medications.
Services Often Not Covered or PaSpecializedered:
- Specialized Fertility Treatments: Procedures like IVF or ICSI are typically not fully covered, leading many to seek private healthcare or insurance.
- Certain Mental Health Services: While basic counselling ispecializedered, specialized psychological or psychiatric services may require private insurance.
- Cosmetic Procedures: Any non-essential procedure, such as cosmetic surgery, is not covered.
- Dental and Vision Care: Most dental and vision care, including regular check-ups and corrective lenses, require additional private insurance.
Knowing the extent and limits of coverage helps women in Canada navigate their healthcare options more effectively.
Steps to Access Healthcare in Canada for Women
To ensure optimal healthcare outcomes, women in Canada should follow key steps when accessing healthcare services. Navigating these steps ensures women can access the full range of healthcare services.
- Health Insurance Registration: Secure a provincial health insurance card to access public healthcare services. Each province has its registration process and criteria.
- Finding a HealUtilizeProvider: Utilize provincial resources to find a family doctor. Health Care Connect helps match patients with local doctors in provinces like Ontario.
- Regular Health Check-Ups: Schedule and attend regular check-ups for preventive care. These can include screenings for cancer, heart health assessments, and discussions about mental health.
- Referral to specialized: For specialized care (like gynaecologists, endocrinologists, etc.), a referral from a family doctor is typically required.
- Urgent Care Needs: Women can visit walk-in clinics or hospital emergency rooms for immediate medical attention.
- Private Insurance Consideration: For services not covered by public healthcare, consider purchasing private health insurance for additional coverage.
Common Barriers Faced by Women in Accessing Healthcare in Canada
Women in Canada face several barriers to accessing healthcare, which can impact their health and wellness; addressing these barriers is critical for improving healthcare access and outcomes for all women in Canada.
- Geographical Challenges: Women in remote or rural areas often have specializedess to specialized healthcare facilities and providers.
- Wait Times for Services: There can be significant wait times for certain procedures and specialist appointments, impacting timely access to care.
- Cultural and Language Differences: Non-native speakers and women from diverse cultural backgrounds may face difficulties in the healthcare system due to language barriers or cultural insensitivity.
- Economic Constraints: Women from lower socioeconomic backgrounds struggle with access to services that public healthcare doesn’t cover, like certain dental, vision, and mental health services.
- Knowledge and Awareness: A lack of awareness about available health services and how to navigate the healthcare system can be a significant barrier.
Preventive Healthcare in Canada for Women
Preventive healthcare is key to maintaining long-term health and well-being for women in Canada:
- Regular Screenings and Check-ups: This includes mammograms, Pap smears, bone density tests, and blood pressure checks.
- Vaccinations: Staying up-to-date with vaccinations, including those specifically recommended for women at different life stages.
- Health Education: Informative sessions on breast self-exams, nutritional guidance, and family planning.
- Lifestyle Assessments: Regular assessments during doctor visits to discuss lifestyle factors affecting health, such as diet, exercise, and stress management.
Lifestyle and Wellness Tips Specific to Women’s Health
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial for women’s long-term health:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Regular Exercise: Incorporating cardio, strength training, and flexibility exercises.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or mindfulness can be particularly beneficial.
- Prioritizing Sleep: Prioritizing sleep and establishing a regular sleep routine.
- Regular Health Screenings: Staying proactive about health by scheduling regular check-ups and screenings.
How to Advocate for Better Healthcare Services for Women
Advocating for improved healthcare services is vital:
- Stay Informed: Understanding current healthcare policies and how they impact women.
- Community Involvement: Participating in local health committees or advocacy groups.
- Engage with Policymakers: Contacting local representatives to voice concerns and suggestions.
- Support NGOs and Initiatives: Collaborate with organizations working towards better healthcare for women.
- Educate and Empower: Share information and encourage women n to prioritise their healthcare needs.
Access to women’s healthcare in Canada is a complex issue that demands immediate action. Women’s health needs are unique and require special attention. Women in Canada must proactively seek medical services and participate in policy advocacy to ensure their health needs are met effectively. Education, awareness, and policy advocacy are crucial to ensure that healthcare in Canada evolves to meet the diverse needs of all women. It is high time that the healthcare system puts women’s health at the forefront and takes immediate action to address the existing gaps.
Comments are closed.