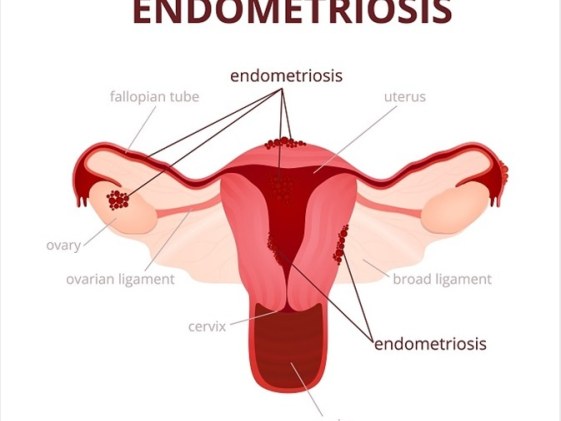
Women are diagnosed with endometriosis when the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus actually grows outside the uterus. When this happens, the ovaries (and possibly the fallopian tubes and tissue lining of the pelvis) are affected.
It is a gynaecological condition associated with menstruation where tissue similar to the lining of the womb is found in other areas of the body, including the fallopian tubes, pelvis, bowel, vagina, and intestines.
It has been alleged that 30 – 40% of Nigerian women (who live in Nigeria) suffer from endometriosis.
There is also a recent study that claims approximately 11% of women and girls in Nigeria unknowingly live with the disorder, even though they show no symptoms, with diagnosis only occurring years later.
1. Cause And Risk Factors
The exact cause of endometriosis is not currently fully understood. Any woman can develop endometriosis, but some risk factors increase the risk. Risk factors such as age as it is most common in women in their 30’s.
Other possible risk factors of endometriosis include;
- Problems with menstrual flow: Menstrual blood enters the fallopian tubes and the pelvis instead of leaving the body in the usual way.
- Surgical scar: Endometrial cells can move during a procedure such as a hysterectomy or C-section.
- Genetics: There may be an inherited component. A woman with a close family member who has endometriosis is more likely to develop endometriosis herself.
- Hormones: Endometriosis is stimulated by the hormone estrogen.
- Immune system: Problems with the immune system can prevent the destruction of extrauterine endometrial tissue.
2. Symptoms
- Severe menstrual cramps
- Long-term lower back and pelvic pain
- Periods lasting longer than 7 days
- Heavy menstrual bleeding where the pad or tampon needs changing every 1 to 2 hours
- Bowel and urinary problems including pain, diarrhea, constipation and bloating
- Bloody stool or urine
- Painful intercourse
3. Diagnosis
Diagnosis can be challenging because there is no single test for evaluation. The only way to truly confirm the condition is by undergoing a surgical laparoscopy.

A surgical laparoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure in which a thin, lighted tube with a miniature camera attached, called a laparoscope, is inserted through a small incision in the pelvic area. It can take many years to receive a diagnosis.
Other possible diagnostic strategies include a pelvic exam, radiologic imaging with ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging, and the use of certain medications including birth control.
4. Treatments
Surgery is possible, but it is normally considered only if other treatments are not effective. Other options include for treatment may include;
- Pain medications: Either over-the-counter (OTC) nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or prescription drugs for the treatment of painful menses. Some doctors also recommend hot water bottle therapy.
- Hormones: Treatment may be with hormonal therapies such as hormonal birth control. Placement of an intrauterine device (IUD) may also be recommended.
- Fertility treatment: Pregnancy may be recommended via in-vitro fertilization (IVF).

